Online MSc in Geographic Information Systems
[ulp id='zqT7PAjnAVG5RK8G']
Definitely, this is one of the best online masters alternatives applied to the geospatial area, and especially served in Spanish.
The Graduate Program MSc (GIS) –Master of Science (Geographical Information Science & Systems), offered and titled by the Salzburg University, Austria, through its Department of Geoinformatics - Z_GIS, Is developed in Spanish by UNIGIS Latin America and its modular content comprises a total score of 120 ECTS.
The program fulfills all the academic requirements demanded by the European Union for a Master / Magister of Science according to the protocol of Bologna. The contents of the curriculum are described below.
The following graphic reflects the conceptual order as the different materials are distributed; As it can be seen, beyond the international validation of the Master, the gradual methodology of application is a very functional conception through nine basic modules equivalent to that comprise the learning of disciplines, domains of tools, and in itself, the flow of Work within a typical GIS project. This is complemented by a module focused on practice and academic work (PATA), as well as optional subjects, offered as electives of modules that address additional highly specialized subjects for the development of the degree project.
The degree work demonstrates the student's ability to independently approach a problem, applying a technical methodology and presenting results in an understandable way, observing the scientific rigor of an academic project.
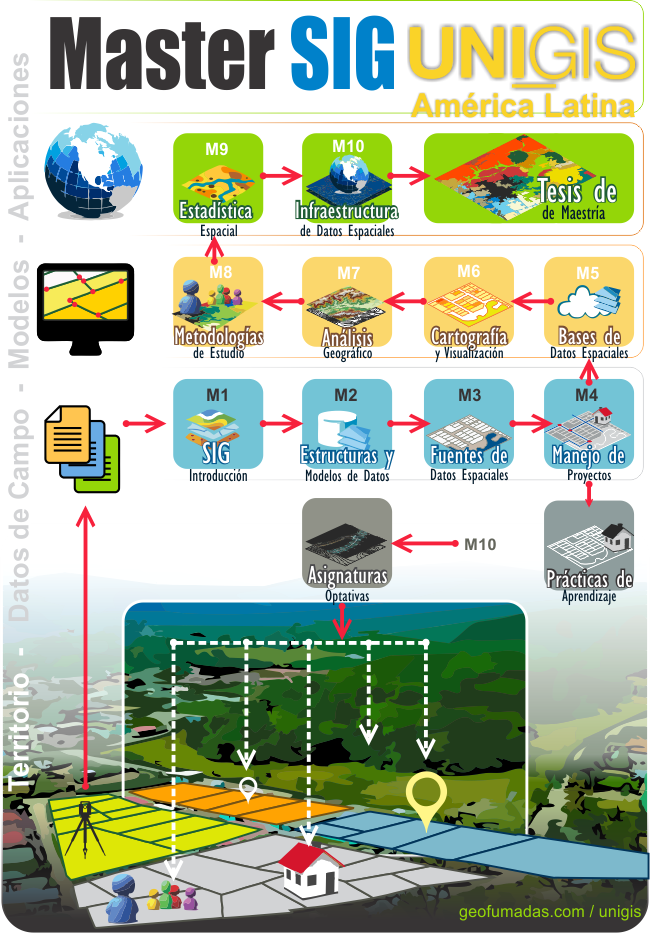
Content of the Modules of the Online Masters
As students develop projects and practices of the Master, they use different Software solutions frequently used in Geo-Engineering. Both proprietary software, such as the one shown below, as well as open source software, which is undoubtedly an unavoidable player in the current ecosystem of solutions.

MódulOr 1: Introduction to GIS
 This module provides a general introduction to the discipline GIScience & technology. It presents GIS terminologies and components, their meaning and history. It also takes a look at the main and current aspects of Geoinformation (GI) technology followed by a discussion on the integration of spatial information in the framework of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). Also noted are the emerging GIS user communities and the ever growing GI industry and marketplace. The module concludes with lessons dedicated to spatial reference systems, emphasizing the importance of positioning and location through coordinates, as well as an introduction to map projections.
This module provides a general introduction to the discipline GIScience & technology. It presents GIS terminologies and components, their meaning and history. It also takes a look at the main and current aspects of Geoinformation (GI) technology followed by a discussion on the integration of spatial information in the framework of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). Also noted are the emerging GIS user communities and the ever growing GI industry and marketplace. The module concludes with lessons dedicated to spatial reference systems, emphasizing the importance of positioning and location through coordinates, as well as an introduction to map projections.
MódulOr 2: Spatial Data Models and Structures
 The module presents spatial concepts and establishes a framework for spatial thinking; In this way the student is provided with a more specific idea of spatial information modeling. It should be noted that most disciplines are non-spatial and some are not aware of the space factor. The module is designed to overcome this deficiency and at the same time show how spatial reasoning and modeling can be implemented in computer programs.
The module presents spatial concepts and establishes a framework for spatial thinking; In this way the student is provided with a more specific idea of spatial information modeling. It should be noted that most disciplines are non-spatial and some are not aware of the space factor. The module is designed to overcome this deficiency and at the same time show how spatial reasoning and modeling can be implemented in computer programs.
MódulOr 3: Acquisition and Spatial Data Sources
 The module focuses on the acquisition of spatial data, their respective principles and technologies. The data quality is directly related to the acquisition methods applied; Therefore, quality concepts and metrics are presented. The rapid increase of geodata and its availability requires not only quality standards, but a reading of its origin and purpose making necessary the management of metadata, among others for efficient search. The module concludes with a discussion on the legal and ethical issues involved.
The module focuses on the acquisition of spatial data, their respective principles and technologies. The data quality is directly related to the acquisition methods applied; Therefore, quality concepts and metrics are presented. The rapid increase of geodata and its availability requires not only quality standards, but a reading of its origin and purpose making necessary the management of metadata, among others for efficient search. The module concludes with a discussion on the legal and ethical issues involved.
MódulO 4: Project Management
 Initially, GIS was considered a challenge that was faced through technological progress. Today it is recognized that the organizational environment is perhaps the key factor for the success of an implementation or a GIS project, however it is important to note that projects are more than organizational frameworks to achieve operational objectives. Looking at the top-down process of business strategic planning, which leads to specific activities in the business plan, it is possible to recognize “project orientation” as a central part. Project management is a discipline where goals are defined and objectives are achieved, <while optimizing the use of resources (time, money, human talent, space, etc.). Topics are discussed in the last part of the course as GIS in organizations and planning, without leaving aside criteria on quality management and legal aspects, concluding with the mention of innovations within the Geoinformation market.
Initially, GIS was considered a challenge that was faced through technological progress. Today it is recognized that the organizational environment is perhaps the key factor for the success of an implementation or a GIS project, however it is important to note that projects are more than organizational frameworks to achieve operational objectives. Looking at the top-down process of business strategic planning, which leads to specific activities in the business plan, it is possible to recognize “project orientation” as a central part. Project management is a discipline where goals are defined and objectives are achieved, <while optimizing the use of resources (time, money, human talent, space, etc.). Topics are discussed in the last part of the course as GIS in organizations and planning, without leaving aside criteria on quality management and legal aspects, concluding with the mention of innovations within the Geoinformation market.
MódulOr 5: Spatial Databases
 The module lays the foundation for organizing data within a DBMS database management system. The content also proposes techniques and tools for the design of a DBMS. Various types and architectures of DBMS are discussed with a special focus on relational / object-oriented and object-relational databases. The use of Structured Query Language (SQL) is also presented both from the point of view of the logic necessary to be able to consult a relational database as well as to define its structure. The second part of the module is dedicated to geoDBMS, that is, Databases that specifically function as repositories for Spatial Data. In particular, the representation of simple objects and the efficient multidimensional access to spatial data are reviewed. It concludes with the presentation of warehousing concepts (large structured repositories) and the benefits of data mining (organized data search).
The module lays the foundation for organizing data within a DBMS database management system. The content also proposes techniques and tools for the design of a DBMS. Various types and architectures of DBMS are discussed with a special focus on relational / object-oriented and object-relational databases. The use of Structured Query Language (SQL) is also presented both from the point of view of the logic necessary to be able to consult a relational database as well as to define its structure. The second part of the module is dedicated to geoDBMS, that is, Databases that specifically function as repositories for Spatial Data. In particular, the representation of simple objects and the efficient multidimensional access to spatial data are reviewed. It concludes with the presentation of warehousing concepts (large structured repositories) and the benefits of data mining (organized data search).
Módulor 6: Cartography and Visualization
 This module focuses on the purpose, parsimony and design. This means what, why and how to communicate spatially. Cartography and GIS are seen here as tools for communication purposes. The recent use of computation in cartography and consecutively in GIS, have considerably changed the design and presentation of maps and diagrams. In the module the foundations of cartography and visual communication are reviewed. The methods of static, dynamic, and terrain visualization, as well as virtual flybys are on the discussion list, also including cutting-edge technologies such as immersed visualization tools and 3D-rendering of space objects.
This module focuses on the purpose, parsimony and design. This means what, why and how to communicate spatially. Cartography and GIS are seen here as tools for communication purposes. The recent use of computation in cartography and consecutively in GIS, have considerably changed the design and presentation of maps and diagrams. In the module the foundations of cartography and visual communication are reviewed. The methods of static, dynamic, and terrain visualization, as well as virtual flybys are on the discussion list, also including cutting-edge technologies such as immersed visualization tools and 3D-rendering of space objects.
MódulO 7: Geographic Analysis
 Spatial analysis is one of the most important components of any GIS system. The process of analyzing geographic data is called geographic analysis or spatial analysis. This is used to evaluate, estimate, predict, interpret and understand geographic information. The module presents the main concepts of spatial analysis and the explanation of functionalities - analysis tools and their classifications, which appear with numerous well-illustrated examples. The module provides particular attention to the matters of map algebra, distance-based analysis, topological network analysis, interpolation, and fuzzy set analysis, among others. The theme concludes with the discussion of models for spatial support in SDSS decision making and how these are based on the results of the geographic analysis.
Spatial analysis is one of the most important components of any GIS system. The process of analyzing geographic data is called geographic analysis or spatial analysis. This is used to evaluate, estimate, predict, interpret and understand geographic information. The module presents the main concepts of spatial analysis and the explanation of functionalities - analysis tools and their classifications, which appear with numerous well-illustrated examples. The module provides particular attention to the matters of map algebra, distance-based analysis, topological network analysis, interpolation, and fuzzy set analysis, among others. The theme concludes with the discussion of models for spatial support in SDSS decision making and how these are based on the results of the geographic analysis.
MódulOr 8: Study Methodologies
 The module provides the student with the guidelines for the compulsory preparation of the Master Thesis, also providing the most important basic knowledge to work in a scientific way. The methodologies include both the bases of the theory of science, as well as useful tips for the bibliographical work and the process of writing itself. The objectives of the module are the introduction to the theory of science, including the place of geoinformatics in the range of scientific disciplines, the facilitation of scientific bibliographic work through the introduction of reading and working techniques, presentation Of the principles of the use of scientific sources and methods, introduction to the formulation and testing of hypotheses, presentation of the essential characteristics for the configuration of scientific works and introduction in presentation techniques (talk, poster).
The module provides the student with the guidelines for the compulsory preparation of the Master Thesis, also providing the most important basic knowledge to work in a scientific way. The methodologies include both the bases of the theory of science, as well as useful tips for the bibliographical work and the process of writing itself. The objectives of the module are the introduction to the theory of science, including the place of geoinformatics in the range of scientific disciplines, the facilitation of scientific bibliographic work through the introduction of reading and working techniques, presentation Of the principles of the use of scientific sources and methods, introduction to the formulation and testing of hypotheses, presentation of the essential characteristics for the configuration of scientific works and introduction in presentation techniques (talk, poster).
MódulO 9: Spatial Statistics
 This module focuses on statistics and its importance for the proper use of GIS, emphasizing the differences between statistics and spatial statistics. Basics of description and statistical analysis are reviewed initially, followed by a chapter on spatial descriptive statistics. Methods and techniques for processing data statistically are also introduced and discussed, such as through spatial autocorrelation, spatial distribution, point pattern analysis, statistical analysis of polygonal data, cluster analysis, and trend surfaces. It also investigates the need and methodologies to arrive at a qualitative data analysis (for example, exploratory spatial data analysis - ESDA). At the end of the module, geo-statistics are presented, with special attention to Kriging and ariography.
This module focuses on statistics and its importance for the proper use of GIS, emphasizing the differences between statistics and spatial statistics. Basics of description and statistical analysis are reviewed initially, followed by a chapter on spatial descriptive statistics. Methods and techniques for processing data statistically are also introduced and discussed, such as through spatial autocorrelation, spatial distribution, point pattern analysis, statistical analysis of polygonal data, cluster analysis, and trend surfaces. It also investigates the need and methodologies to arrive at a qualitative data analysis (for example, exploratory spatial data analysis - ESDA). At the end of the module, geo-statistics are presented, with special attention to Kriging and ariography.
Módulo 10: Spatial Data Infrastructures - IDE
 At present, all over the world, projects are being created in order to build spatial data infrastructures. Its focus is to improve accessibility to geospatial data. With the paradigm shift, moving systems to services, Spatial Data Infrastructures, the market for Spatial Data / Datawarehouses and GeoMarketing, have been pronounced as key terms in the GIS field. This module presents key concepts that support and evaluate the political and economic impact of distributed geo-processing and the OGC (Open GIS Consortium) process. The module also presents the technological and methodological aspects when implementing developments on WMS, WFS, XML and GML among other new standards to globally communicate geoinformation from INTRANET, INTERNET and MOBILE platforms.
At present, all over the world, projects are being created in order to build spatial data infrastructures. Its focus is to improve accessibility to geospatial data. With the paradigm shift, moving systems to services, Spatial Data Infrastructures, the market for Spatial Data / Datawarehouses and GeoMarketing, have been pronounced as key terms in the GIS field. This module presents key concepts that support and evaluate the political and economic impact of distributed geo-processing and the OGC (Open GIS Consortium) process. The module also presents the technological and methodological aspects when implementing developments on WMS, WFS, XML and GML among other new standards to globally communicate geoinformation from INTRANET, INTERNET and MOBILE platforms.
Learning and Academic Work Practices
 Through this module, the student must begin putting into practice the knowledge acquired throughout the program, combined with their professional experience to obtain practical and applied results. It is also intended to encourage independent study for the acquisition of knowledge in specific fields of interest for each student. Finally, the participation of the academic community in conferences, external courses and training, related to the field of GIS, is motivated and recognized.
Through this module, the student must begin putting into practice the knowledge acquired throughout the program, combined with their professional experience to obtain practical and applied results. It is also intended to encourage independent study for the acquisition of knowledge in specific fields of interest for each student. Finally, the participation of the academic community in conferences, external courses and training, related to the field of GIS, is motivated and recognized.
ModuloS Electives
 The student will be able to choose modules specialized in different fields of application in GIS according to the following academic offer. Most of the elective modules have a specific focus on the application of GIS in Latin America.
The student will be able to choose modules specialized in different fields of application in GIS according to the following academic offer. Most of the elective modules have a specific focus on the application of GIS in Latin America.
Each elective module grants the student six (6) ECTS credits.
ArcGIS for Server Geoprocessing with Python GIS and Remote Sensing
SIG in Public Health
SIG, Risks and Disasters
SIG in Communal / Territorial Development
SIG in Community Services
SIG and Agriculture
SIG and Environment
ORACLE Spatial
Application Development (Using Java) Developing Applications with OSM
 Master's Thesis
Master's Thesis
The student will choose his research topic to develop a final GIS project, according to his interest, applying the knowledge acquired throughout the program.
UNIGIS Latin America offers Education from distance in GIS in Spanish for professionals from Latin America. Students qualify for a European Master of Science (M.Sc.) in GIS, Master of GIS; or the UNIGIS Professional, Specialization in GIS, with the University of Salzburg, Austria and join more than 500 graduates who have become leaders and experts in institutions, organizations and companies at national, regional and global level.
At the regional level, UNIGIS has nodes in different Latin American countries, at least in the following countries and Universities:
- Argentina: University of Belgrano (UB)
- Brazil: University of the State of Rio de Janeiro (UERJ)
- Chile: University of Santiago de Chile (USACH)
- Colombia: ICESI University
- Ecuador: San Francisco University of Quito (USFQ)
- Mexico: Autonomous Metropolitan University (UAM)
- Peru: National University Federico Villarreal (UNFV)

It is probable that the Master GIS Online presented here presents you with doubts such as:
- How do I register?
- How long does the mastery last?
- How much does it cost and what payment methods are available?
- Is it totally online or blended?
- When does the next cycle begin?
Fill out the form and you will be sent information on how to proceed.
[ulp id='zqT7PAjnAVG5RK8G']







I am Brazilian and would like to receive more information about this teacher.
Would you be kind enough to inform me about the costs and if there is any type of scholarship or discount.
For Ecuador, how is the Master's degree endorsed?
Please I need information about the master's degree
I am very interested in receiving information about the master's degree.
Thank you
j'ai besoin d'avoir des informations sur ce master. Merci
I am interested in knowing the costs and if there is any type of scholarship, discount or financing.
Is all the masters online?
In Mexico, how do you guarantee the Master's degree?
I need to know detailed information about naestria
I'm interested in GIS mastery
Hello, I think it's an excellent program, but I would like to know the costs and if they handle some type of scholarship.
Good evening I would like to participate, but I have the cost, I will not have a scholarship to 50% to apply and I do not have the program I have tried to download it and I can not.
Thank you
Esteban
Information costs please. Thank you
I want a master's info .. Thanks
I would like to receive more information about the mastery.
Hello! I would like to receive more information about the master's degree.
regards
I AM VERY INTERESTED IN RECEIVING INFORMATION ABOUT THE MASTER