GIS software - described in 1000 words
The recent month of May, 1.2 version was released Of this brief but admirable document that with that name seems to mock the complexity of the Software for the management of spatial data.
It is written by Stefan Steiniger and Robert Weibel of the University of Calgary in California and the University of Zurich respectively. In the end they give credits to some secondary sources.
After a brief introduction, which explains the basic application trends of the GIS software, the document contains 4 topical topics:
GIS Software: Concepts
Here we differentiate between the two main ways of representing the data: Raster and Vector.
Then they masterfully apply the old principle of "An image is worth a thousand words" and present the OpenJump screen to express the most common sections of a GIS tool:
- The function menu
- Navigation tools
- The layer frame
- The editing tools
- The spatial view of the map
- Tabular view of attributes

Basic routines that accompany the GIS Software
In this section there is a list of 9 basic functions that a user requires of a tool:
- Create data
- Edit, In case the data has changed
- To stock, After having made the changes
- Visualize Data from other sources
- To integrate Data from other sources with existing ones
- Consult Based on criteria
- Analyze Data and create results
- Handle And transform data resulting from analysis
- Publish Output results in the form of maps
 This process I had previously raised in Six steps When I did the Manifold manual, in this case they expand what is data construction separating those that are obtained with other tools and analysis, separating the simple query, analysis of results and transformation to new data.
This process I had previously raised in Six steps When I did the Manifold manual, in this case they expand what is data construction separating those that are obtained with other tools and analysis, separating the simple query, analysis of results and transformation to new data.
- Construction (Create, View)
- Analysis (Consult, Analyze, Manipulate)
- Publishing (Publish)
- Edit (Edit)
- Administration (Store)
- Exchange (Integrate)
GIS Software Categories
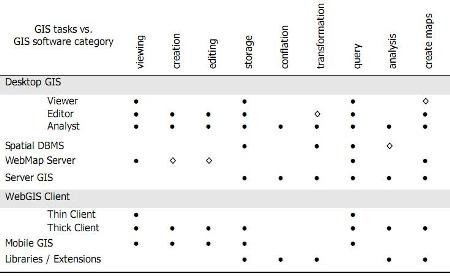
In this section different 7 categories are separated depending on the specialty, among them:
- GIS for Desktop (Desktop)
Viewer
Editor
Analyst - Spatial Data Handler
- Web map server
- Server GIS
- Web GIS Client
Lightweight (Like Google Maps)
Heavy (Like Google Earth) - GIS for Mobile (Mobile GIS)
- GIS libraries and extensions
Apart from a chart is included a comparative table in which the 9 functionalities above are crossed with the specialty categories of the software.
GIS Software Manufacturers and Projects
In this one mention the main tendencies of manufacture of software, the commercial and the free.
The commercial refers to AutoDesk, Bentley, ESRI, GE (Small World), and Pitney Bowes (Mapinfo)
And among free software mention is made of MapServer, GeoServer, PostGIS, Quantum GIS, and gvSIG.
_____________________________________
My respects, one day I would like to write like this.






I do not fit for anything
The information seems good but it is bad I need to know what each tool does
I did not like
I think it's very good